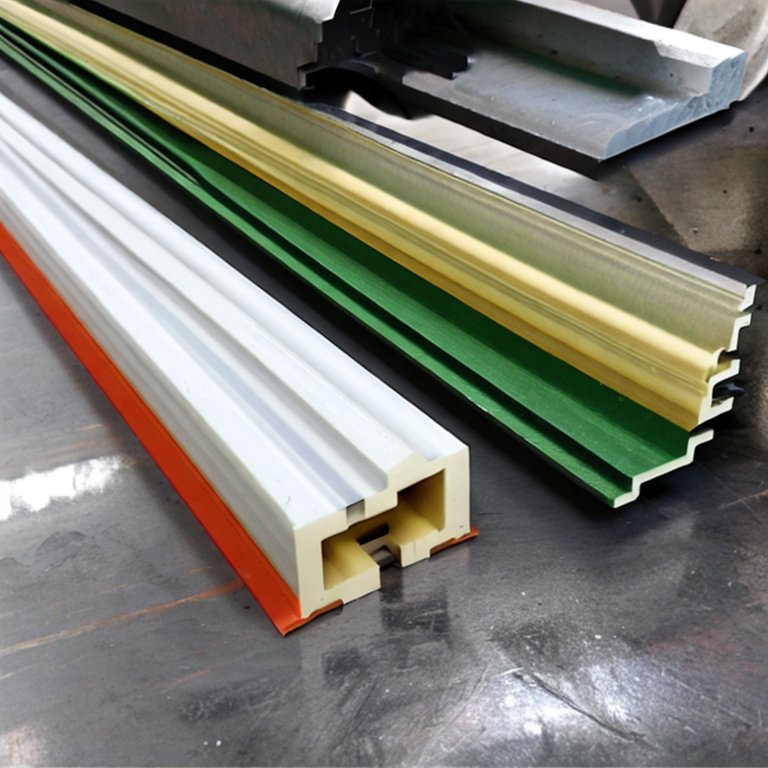
Laminating plastic is bonding one or more layers of plastic film together to create a single composite material. The process has been widely used in various industries due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Laminating plastic has become essential in many industries, including packaging, construction, and automotive, due to its strength, durability, and barrier properties. However, the growing concern over plastic waste and its impact on the environment has raised questions about the sustainability of laminated films.

Types of Laminating Plastic:
There are several types of laminating plastic used in different industries, including polyethene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyester (PET), and nylon. Each type has its own unique properties, making it suitable for different applications. PE is commonly used for food packaging and industrial applications, while PP is popular for its resistance to chemicals and moisture. PVC is a durable and versatile plastic commonly used in the construction industry. PET is a popular choice for packaging due to its clarity and strength, while nylon is often used for industrial applications due to its high strength and durability.
Industrial Usage:
Laminating plastic is widely used in various industries, including packaging, automotive, construction, and textiles. In the packaging industry, laminated films produce flexible packaging materials for food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. The automotive industry uses laminated plastic for interior parts such as dashboards and door panels. The construction industry uses laminated plastic for roofing, flooring, and insulation. Textile manufacturers use laminated plastic for waterproof and windproof fabrics.
Application Areas:
Laminating plastic is used in various applications, including food packaging, automotive parts, construction materials, and textiles. In food packaging, laminated films are used to create a barrier to protect the contents from moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants. The automotive industry uses laminated plastic for interior parts such as dashboards and door panels. The construction industry uses laminated plastic for roofing, flooring, and insulation. Textile manufacturers use laminated plastic for waterproof and windproof fabrics.
Consumer Product Examples:
Laminated plastic is used in various consumer products, including food packaging, cosmetic packaging, and electronics. Examples of laminated plastic in food packaging include snack bags, cereal box liners, and juice pouches. Cosmetic packagings such as shampoo bottles and lotion tubes are also commonly made from laminated plastic.
Material Properties:
Laminating plastic offers several benefits over traditional plastic materials, including increased durability, moisture resistance, and improved strength. Laminated plastic also provides a barrier to protect the contents from moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants. The properties of laminated plastic can be customised to meet specific application requirements, such as improved flexibility, strength, and clarity.
Future Trends in regards to Recycling:
As the demand for sustainable materials grows, there is an increasing focus on recycling laminated plastic. Recycling technologies have been developed to recover materials from laminated plastic, including mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and pyrolysis. Mechanical recycling involves shredding and melting plastic to create new products. Chemical recycling consists in breaking down the plastic into its chemical components and using them to develop new materials. Pyrolysis involves heating the plastic to high temperatures to break it into chemical components.
The future market prognosis for laminating plastic is favourable, with the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials driving innovation in the industry. Manufacturers are investing in new technologies to develop more environmentally friendly laminated films that are easier to recycle. The use of bio-based materials and the development of new recycling technologies are expected to shape the future of the laminating plastic industry.
Market Price Developments:
Various factors, including the cost of raw materials, production costs, and demand influence the market price of laminating plastic. The price of laminating plastic has risen in recent years due to the increasing demand for sustainable materials and the rising cost of raw materials. However, production technology advancements have helped reduce production costs, making laminated plastic more affordable for various industries.
Global Impact:
The global impact of laminating plastic is significant, with the packaging industry being the largest laminated film user. The growing demand for packaged food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods drives the demand for laminated plastic. Laminated plastic also plays a vital role in the automotive and construction industries. However, the environmental impact of laminated plastic has become a growing concern due to the non-biodegradable nature of some plastic materials.
Laminating plastic’s impact on recycling
When discussing laminating plastic and its impact on recycling, it’s essential to mention that laminated films are challenging to recycle due to the combination of different materials. In many cases, the materials used in laminating plastic cannot be easily separated, making recycling difficult. This creates significant environmental challenges as laminating plastic can take hundreds of years to decompose, accumulating waste in landfills and oceans.
However, advancements in recycling technologies have helped to address this challenge, and many companies are now investing in new technologies to recycle laminated plastic. These technologies use innovative methods such as chemical recycling, where the laminated films are broken down into their constituent materials and then re-used to make new products. This approach can help reduce waste and the environmental impact of laminated plastic.
Another important aspect to consider is the circular economy, which emphasises reusing and recycling materials. In a circular economy, laminated plastic can be designed and produced in a way that enables easy separation of its constituent materials, making it easier to recycle. Additionally, bio-based materials and compostable laminating films are gaining popularity, which can significantly reduce the environmental impact of laminating plastic.
Laminating plastic:
In conclusion, laminating plastic is a widely used and versatile material with several advantages, including increased strength, durability, and barrier properties. However, the growing concern over plastic waste and its environmental impact has led to increased scrutiny and regulations on laminated films. As we move towards a more sustainable future, we must explore alternative materials that offer the same benefits as laminating plastic while minimising their environmental impact. By working together, we can create a more circular economy that prioritises sustainability and reduces our reliance on non-renewable resources.