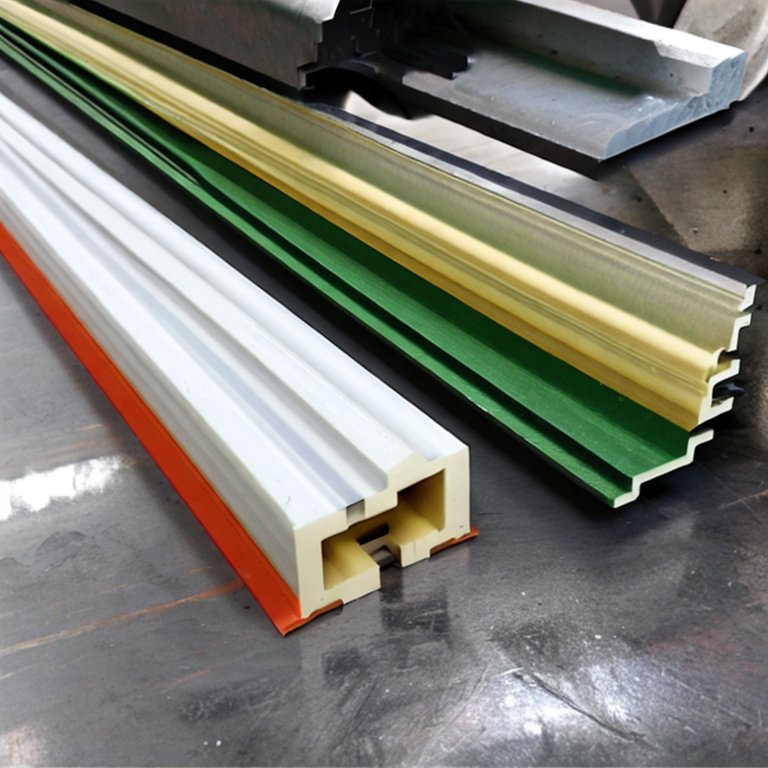
Thermoforming plastic is a manufacturing process used to create a wide range of plastic products. It involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable and then forming it into the desired shape using a mould or vacuum forming. This process is commonly used in a variety of industries, including food packaging, automotive, and medical devices.
Thermoforming plastics have become ubiquitous, found in everything from food packaging to automotive interiors. Thermoforming Plastics offer numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, versatility, and customisability. The widespread use of thermoformed plastics has raised concerns about their environmental impact and limited recyclability.

Types of Thermoforming Plastics
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET is a widely used thermoplastic material that is commonly used for making bottles, trays, and other packaging materials. It is known for its high strength, durability, and chemical resistance. PET is also recyclable, which makes it an eco-friendly option for packaging.
- Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is another widely used thermoforming plastic known for its high strength, rigidity, and insulation properties. It is commonly used for making food packaging, disposable cups, and cutlery. PS is also recyclable, but its recycling rate is relatively low.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is a versatile thermoplastic material commonly used in construction, medical devices, and consumer goods. It is known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals. PVC is also recyclable, but its recycling rate is relatively low.
- Polypropylene (PP)
PP is a thermoplastic material that is commonly used for making food packaging, medical devices, and consumer goods. It is known for its high strength, durability, and chemical resistance. PP is also recyclable, which makes it an eco-friendly option for packaging.

Industrial Usage
Thermoforming plastics are used in a variety of industries, including food packaging, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. In the food packaging industry, thermoforming plastics are used to create trays, containers, and other packaging materials that protect food and extend its shelf life. In the automotive industry, thermoforming plastics are used to create interior and exterior components that are lightweight and durable. In the medical device industry, thermoforming plastics are used to create safe, sterile, and disposable devices. In the consumer goods industry, thermoforming plastics create a wide range of products, including toys, electronics, and packaging materials.
Application Areas
Thermoforming plastics are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Food packaging: Thermoforming plastics are commonly used to create trays, containers, and other packaging materials that protect food and extend its shelf life.
- Medical devices: Thermoforming plastics are used to create devices that are safe, sterile, and disposable, including test kits, diagnostic devices, and surgical tools.
- Automotive: Thermoforming plastics are used to create interior and exterior components that are lightweight, durable, and aesthetically pleasing.
- Consumer goods: Thermoforming plastics are used to create a wide range of products, including toys, electronics, and packaging materials.
Consumer Product Examples
Thermoforming plastics are used in a variety of consumer products, including:
- Food packaging: Thermoforming plastics are used to create trays, containers, and other packaging materials that protect food and extend its shelf life.
- Disposable cups and cutlery: Thermoforming plastics are used to create disposable cups, cutlery, and other single-use items.
- Medical devices: Thermoforming plastics are used to create devices that are safe, sterile, and disposable, including test kits, diagnostic devices, and surgical tools.
- Electronics: Thermoforming plastics are used to create a wide range of electronic products
Market Price Developments
The price of thermoforming plastics is influenced by a variety of factors, including the cost of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and demand from different industries. The price of thermoforming plastics can fluctuate depending on the availability of raw materials and changes in the global market.
Global Impact
The use of thermoforming plastics significantly impacts the environment, particularly in terms of waste and pollution. Thermoforming plastics can contribute to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, leading to environmental degradation and harm to wildlife. Thermoforming plastics have also been linked to greenhouse gas emissions, which can contribute to climate change.
To address these concerns, many governments and organisations worldwide have implemented regulations and initiatives aimed at reducing the use of plastics and promoting recycling. For example, the European Union has set targets to reduce plastic waste and increase recycling rates, while many countries have implemented plastic bag bans or taxes.
Future Market Prognosis
The thermoforming plastics market is expected to grow in the coming years, driven by increasing demand from industries such as food packaging, automotive, and consumer goods. The growing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable materials is also expected to drive the development of new, eco-friendly thermoforming plastics.
In addition, the adoption of new technologies such as 3D printing and automation is expected to streamline the thermoforming process and increase efficiency. Bioplastics, made from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, are also expected to increase in the coming years, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional thermoforming plastics.
However, the market for thermoforming plastics may face challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices, increasing competition from alternative materials, and the need to address environmental concerns. To remain competitive and sustainable, manufacturers will need to continue to innovate and develop new products and processes that meet the evolving needs of their customers and the market.
Thermoforming’s impact on recycling
To expand on the topic of how thermoforming plastics relate to recycling, it’s important to note that thermoformed plastics can be recycled and repurposed into new products. However, the recycling process for thermoformed plastics can be more complex than other plastic materials due to their unique properties and the presence of additives such as colourants and fillers.
One of the most common methods of recycling thermoformed plastics is mechanical recycling, which involves shredding the plastic into small pieces and melting them to create new products. However, this process can be limited by the type of thermoformed plastic being recycled, as some types may be more difficult to process. It may require additional steps such as separation and cleaning.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in developing new methods of recycling thermoformed plastics, such as chemical recycling and pyrolysis. These methods involve breaking down the plastic at a molecular level, allowing it to be used as feedstock for new plastics or other materials.
Overall, the recycling of thermoformed plastics presents both challenges and opportunities for the plastics industry. By developing new recycling methods and increasing the use of recycled thermoformed plastics in new products, the industry can work towards a more sustainable and circular economy, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Process advantages and disadvantages
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that involves heating a plastic sheet to a pliable temperature and then forming it into a desired shape using a mould or tool. Thermoforming plastics are widely used in various industries due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and customisation ability.
Advantages of Thermoforming Plastics
One of the primary advantages of thermoforming plastics is their cost-effectiveness. The process is relatively simple and efficient, allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities of products quickly and at a low cost. Additionally, thermoforming plastics offer a wide range of design and customisation options, making them ideal for various applications.
Thermoformed plastics are also lightweight, making them a popular choice for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where weight reduction is critical. They are also durable and have good impact resistance, making them ideal for packaging and consumer goods applications.
Disadvantages of Thermoforming Plastics
One of the main disadvantages of thermoforming plastics is their limited recyclability. As mentioned earlier, the recycling process for thermoformed plastics can be more complex than other plastic materials, making recycling more difficult and expensive.
Thermoformed plastics are less strong and heat-resistant than other materials such as injection-moulded plastics or composites. This can limit their use in certain applications, particularly those that require high strength or temperature resistance.
Thermoforming plastics:
Thermoforming plastics have revolutionised the manufacturing industry, offering numerous advantages such as cost-effectiveness, versatility, and customisability. However, their limited recyclability and potential environmental impacts must be addressed.
As we look to the future, we must continue to develop sustainable alternatives to traditional thermoforming plastics, such as bioplastics and recycled plastics. By working together, we can create a more sustainable and responsible plastics industry that benefits both our economy and the environment.